Obiettivi | Certificazione | Contenuti | Tipologia | Prerequisiti | Durata e Frequenza | Docenti | Modalità di Iscrizione | Calendario

Il corso Architecting on AWS (ARCHIT) è progettato per insegnare ai partecipanti come ottimizzare l’utilizzo dei servizi AWS per progettare soluzioni architetturali sicure, affidabili ed efficienti. Questo corso è rivolto a professionisti IT e copre i principali concetti, principi e best practice per la progettazione di soluzioni basate su AWS.
Il corso fornisce una panoramica dettagliata dei principali servizi AWS, tra cui Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, Amazon VPC e altri servizi relativi all’architettura, allo storage, alla sicurezza e alla gestione delle applicazioni.
I partecipanti impareranno come progettare architetture scalabili e flessibili che si adattano alle esigenze delle loro applicazioni e alle variazioni del carico di lavoro, sfruttando al meglio i servizi AWS nonché apprenderanno le tecniche per migliorare le prestazioni delle applicazioni, tra cui l’uso di caching, la distribuzione del contenuto e l’ottimizzazione del trasporto dei dati.
Attraverso lezioni teoriche, esercizi pratici e casi di studio, i partecipanti acquisiranno una conoscenza approfondita dei principi e delle best practice per la progettazione di soluzioni su AWS e saranno in grado di applicarli in scenari reali.
Il corso contribuisce alla preparazione dell’esame di Certificazione AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate, fornendo informazioni sulle aree tematiche coperte dall’esame e suggerimenti per la preparazione.
Sintesi Statistica
- Corsi realizzati: 32
- Numero Corsisti: 176
- Superamento Esame: 97,15%
Contattaci ora per ricevere tutti i dettagli e per richiedere, senza alcun impegno, di parlare direttamente con uno dei nostri Docenti (Clicca qui)
oppure chiamaci subito al nostro Numero Verde (800-177596)
Obiettivi del corso
Di seguito una sintesi degli obiettivi principali del corso Architecting on AWS (ARCHIT):
- Ottimizzazione dell’Utilizzo dei Servizi AWS: Imparare a massimizzare l’uso dei servizi AWS per creare soluzioni architetturali sicure ed efficienti.
- Progettazione di Architetture Scalabili e Flessibili: Acquisire competenze per progettare architetture che si adattino alle esigenze delle applicazioni e alle variazioni del carico di lavoro, utilizzando al meglio i servizi AWS.
- Miglioramento delle Prestazioni delle Applicazioni: Apprendere tecniche per potenziare le prestazioni delle applicazioni, inclusi l’utilizzo di caching, la distribuzione del contenuto e l’ottimizzazione del trasporto dei dati.
- Conoscenza Approfondita dei Principi e Best Practice AWS: Attraverso lezioni, esercizi pratici e casi di studio, i partecipanti acquisiranno una conoscenza approfondita dei principi e delle best practice per la progettazione di soluzioni su AWS.
- Panoramica dei Servizi AWS: Fornire una panoramica dettagliata dei principali servizi AWS, tra cui Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, Amazon VPC e altri servizi relativi all’architettura, allo storage, alla sicurezza e alla gestione delle applicazioni.
Certificazione del corso
Esame AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate; L’esame di certificazione AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate (SAA-C03) è volto a valutare le competenze dei candidati nella progettazione, distribuzione e gestione di soluzioni scalabili, altamente disponibili su AWS. I candidati devono dimostrare una conoscenza approfondita delle migliori pratiche e delle soluzioni AWS per affrontare problemi comuni e specifici, coprendo argomenti come l’architettura delle soluzioni, il networking, la sicurezza, il costo e la pianificazione delle risorse.
Contenuti del corso
Module 1: Architecting Fundamentals
- AWS services
- AWS infrastructure
- AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Hands-on lab: Explore and interact with the AWS Management Console and AWS Command Line Interface
Module 2: Account Security
- Principals and identities
- Security policies
- Managing multiple accounts
Module 3: Networking 1
- IP addressing
- VPC fundamentals
- VPC traffic security
Module 4: Compute
- Compute services
- EC2 instances
- Storage for EC2 instances
- Amazon EC2 pricing options
- AWS Lambda
- Hands-On Lab: Build your Amazon VPC infrastructure
Module 5: Storage
- Storage services
- Amazon S3
- Shared file systems
- Data migration tools
Module 6: Database Services
- Database services
- Amazon RDS
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Database caching
- Database migration tools
- Hands-on Lab: Create a database layer in your Amazon VPC infrastructure
Module 7: Monitoring and Scaling
- Monitoring
- Alarms and events
- Load balancing
- Auto scaling
- Hands-on Lab: Configure high availability in your Amazon VPC
Module 8: Automation
- AWS CloudFormation
- Infrastructure management
Module 9: Containers
- Microservices
- Containers
- Container services
Module 10: Networking 2
- VPC endpoints
- VPC peering
- Hybrid networking
- AWS Transit Gateway
Module 11: Serverless
- What is serverless?
- Amazon API Gateway
- Amazon SQS
- Amazon SNS
- Amazon Kinesis
- AWS Step Functions
- Hands-on Lab: Build a serverless architecture
Module 12: Edge Services
- Edge fundamentals
- Amazon Route 53
- Amazon CloudFront
- DDoS protection
- AWS Outposts
- Hands-On Lab: Configure an Amazon CloudFront distribution with an Amazon S3 origin
Module 13: Backup and Recovery
- Disaster planning
- AWS Backup
- Recovery strategies
- Hands-on Lab: Capstone lab – Build an AWS Multi-Tier architecture. Participants review the concepts and services learned in class and build a solution based on a scenario. The lab environment provides partial solutions to promote analysis and reflection. Participants deploy a highly available architecture. The instructor is available for consultation.
Tipologia
Corso di Formazione con Docente
Docenti
I docenti sono Istruttori accreditati Amazon AWS e certificati in altre tecnologie IT, con anni di esperienza pratica nel settore e nella Formazione.
Infrastruttura laboratoriale
Per tutte le tipologie di erogazione, il Corsista può accedere alle attrezzature e ai sistemi presenti nei Nostri laboratori o direttamente presso i data center del Vendor o dei suoi provider autorizzati in modalità remota h24. Ogni partecipante dispone di un accesso per implementare le varie configurazioni avendo così un riscontro pratico e immediato della teoria affrontata. Ecco di seguito alcuni scenari tratti dalle attività laboratoriali:
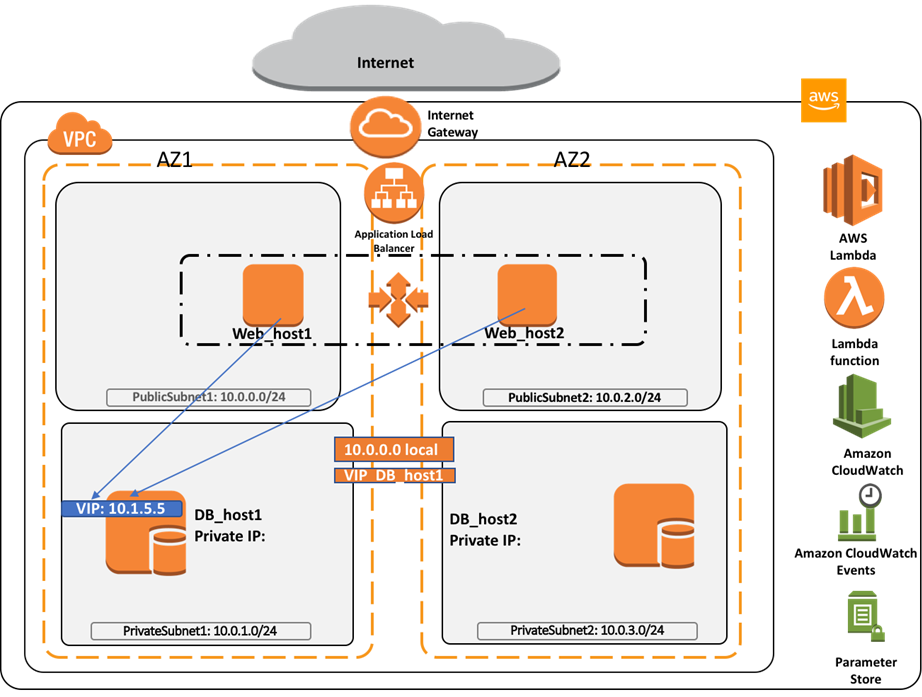
Dettagli del corso
Prerequisiti
Si consiglia la partecipazione al Corso AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials e al Corso AWS Technical Essentials;
Durata del corso
- Durata Estensiva 30 Ore;
- Durata Intensiva 3gg;
Frequenza
Varie tipologie di Frequenza Estensiva ed Intensiva.
Date del corso
- Architecting on AWS (Formula Intensiva) – 20/05/2024 – 09:00 – 17:00
- Architecting on AWS (Formula Estensiva Serale) – 03/06/2024 – Lun. Mer. Ven. 18:30/21:30
- Architecting on AWS (Formula Intensiva) – 17/06/2024 – 09:00 – 17:00
- Architecting on AWS (Formula Intensiva) – 15/07/2024 – 09:00 – 17:00
- Architecting on AWS (Formula Intensiva) – 16/09/2024 – 09:00 – 17:00
- Architecting on AWS (Formula Intensiva) – 14/10/2024 – 09:00 – 17:00
- Architecting on AWS (Formula Intensiva) – 18/11/2024 – 09:00 – 17:00
- Architecting on AWS (Formula Intensiva) – 16/12/2024 – 09:00 – 17:00
Modalità di iscrizione
Le iscrizioni sono a numero chiuso per garantire ai tutti i partecipanti un servizio eccellente. L’iscrizione avviene richiedendo di essere contattati dal seguente Link, o contattando la sede al numero verde 800-177596 o inviando una richiesta all’email [email protected].


