Obiettivi | Certificazione | Contenuti | Tipologia | Prerequisiti | Durata e Frequenza | Docenti | Modalità di Iscrizione | Calendario

Il Corso CBRCOR Performing CyberOps Using Cisco Security Technologies, rappresenta il pilastro fondamentale del percorso tecnologico e di certificazione CyberOPS Professional. Esso infatti prepara il partecipante all’esame Core della Certificazione Cisco CyberOps Professional (Esame 350-201). In questo corso si acquisiranno le competenze, i metodi e le tecniche di automazione delle operazioni di sicurezza informatica. Le conoscenze acquisite in questo corso prepareranno il partecipante per il ruolo di analista della sicurezza delle informazioni in un team SOC (Security Operations Center). Si impareranno i concetti fondamentali e avanzati della cyber security e la loro applicazione in scenari del mondo reale e come sfruttare i playbook nella formulazione di una risposta agli incidenti (IR). Il corso mostra come utilizzare l’automazione per la sicurezza utilizzando piattaforme cloud e una metodologia SecDevOps. Si impareranno le tecniche per rilevare gli attacchi informatici, analizzare le minacce e formulare raccomandazioni appropriate per migliorare la sicurezza informatica in contesti produttivi. Il Corso contribuisce alla preparazione dell’esame di Certificazione Cisco DevNet Professional (Esame 350-901).
Contattaci ora per ricevere tutti i dettagli e per richiedere, senza alcun impegno, di parlare direttamente con uno dei nostri Docenti (Clicca qui)
oppure chiamaci subito al nostro Numero Verde (800-177596)
Obiettivi del corso
Di seguito una sintesi degli obiettivi principali del Corso CBRCOR Performing CyberOps Using Cisco Security Technologies:
- Comprendere l’automazione delle operazioni SOC e l’uso di playbook per la risposta agli incidenti.
- Applicare concetti avanzati di cybersecurity in scenari reali.
- Utilizzare l’automazione della sicurezza su piattaforme cloud e adottare pratiche SecDevOps.
- Rilevare e analizzare minacce informatiche per migliorare la sicurezza.
- Prepararsi per il ruolo di analista di sicurezza delle informazioni in un SOC.
Certificazione del corso
Esame 350-201 CBRCOR Performing CyberOps Using Cisco Security Technologies;
Esame parte della Certificazione CyberOps Professional. Il programma di certificazione Cisco CyberOps Professional prepara per i ruoli professionali Senior di Security operations analyst, Security incident responder e Forensic analyst all’interno di centri operativi di sicurezza (SOC). Questa certificazione è indirizzata a figure professionali con alcuni anni di esperienza nelle tematiche di sicurezza legate alle infrastrutture di rete complesse. In particolare l’esame 350-201 CBRCOR testa competenze su argomenti quali: incident response, security cloud platforms, hardening machine, security diagnose gaps, network segmentation, SecDevOps, threat intelligence platform, security data management, security data analytics, network analysis, troubleshoot detection rules, compromise (IOCs) and indicators of Attack (IOAs), reverse engineering, investigate endpoint intrusion, interpret basic scripts and common data formats, interpret API authentication mechanisms, utilize bash commands e altro ancora.
Contenuti del corso
- Understanding Risk Management and SOC Operations
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance
- Security Regulatory Requirements
- Security Policy
- Protected Information
- Risk Analysis and Insurance
- SOC Services, Operations, and Automation
- SOC Service Models
- Understanding Analytical Processes and Playbooks
- Security Analytics
- SOC Playbook
- SOC Automation and Workflow
- Incident Response Concepts, Metrics, and Workflow
- Documenting Security Incidents in Cases
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response
- Cisco SecureX Orchestration Workflows
- Explore Cisco SecureX Orchestration
- Splunk Enterprise and Phantom Overview
- Explore Splunk Phantom Playbooks
- Investigating Packet Captures, Logs, and Traffic Analysis
- Identity Access Management Logs
- Artifacts and Traffic Streams in a Packet Capture
- Examine Cisco Firepower Packet Captures and PCAP Analysis
- Nextgen Firewall and IPS Logs
- Dissecting Suspicious Requests
- Network Traffic Analysis Using NetFlow Analytics
- Detecting and Enforcing DLP On-the-Wire
- Cisco AMP Architecture
- Cisco Web Security Appliance
- Network DNS Logs
- Cisco Email Security Appliance
- Email Security Logs (Not Detection-Based)
- Cisco Umbrella Reports
- Validate an Attack and Determine the Incident Response
- Investigating Endpoint and Appliance Logs
- Cisco ISE Monitoring, Reporting, and Alerting
- Cisco Advanced Malware Protection
- Cisco Threat Grid
- Submit a Malicious File to Cisco Threat Grid for Analysis
- Endpoint Logs from Non-Detection Sources
- Server DNS Logs
- Internet of Things
- Web Security Logs
- Endpoint Data Loss Protection
- Endpoint-Based Attack Scenario Referencing MITRE ATTACK®
- Understanding Cloud Service Model Security Responsibilities
- Evolution of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Service Models
- Security Responsibilities in the IaaS Service Model
- Security Responsibilities in the PaaS Service Model
- Security Responsibilities in the SaaS Service Model
- Cloud Deployment Models
- Key Security Controls in SaaS
- Cloud Access Security Broker
- Cisco Cloudlock
- Cloud Security Regulations and References
- Understanding Enterprise Environment Assets
- Asset Management
- Remediating Vulnerabilities and the SOC
- Assessing Vulnerabilities
- Patch Management
- Data Storage and Protecting Data Privacy
- Multi-Factor Authentication
- Zero Trust Model
- Evaluate Assets in a Typical Enterprise Environment
- Implementing Threat Tuning
- Security Tuning Governance Policy
- Tuning Security Controls Rules, Filters, and Policies
- Determining If a Rule Is Defective
- Anatomy of a Snort Rule
- Explore Cisco Firepower NGFW Access Control Policy and Snort Rules
- Troubleshooting Detection Rules
- Recommending Scenarios for Tuning
- Threat Research and Threat Intelligence Practices
- Cyber Threat Intelligence Overview
- Cyber Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
- Cyber Threat Intelligence Data Sources
- Indicators of Compromise and Indicators of Attack
- Security Intelligence Reports
- Investigate IOCs from Cisco Talos Blog Using Cisco SecureX
- Cyber Attribution
- Cyber Threat Intelligence Tools
- Security Intelligence in a TIP Platform
- Using Indicator Analysis to Reveal Hidden Infections
- Explore the ThreatConnect Threat Intelligence Platform
- Track the TTPs of a Successful Attack Using a TIP
- Understanding APIs
- API Overview
- CSV, HTML, and XML Data Encoding
- JSON Data Encoding
- YAML Data Serialization Standard
- HTTP-Based APIs
- RESTful APIs vs. Non-RESTful APIs
- Cisco pxGrid
- HTTP-Based Authentication
- Postman
- Query Cisco Umbrella Using Postman API Client
- RESTCONF
- NETCONF
- Google RPC
- Data Modeling with YANG
- STIX and TAXII Specifications
- Role of APIs in Cisco Security Solutions
- Python Fundamentals
- Python Virtual Environments
- Fix a Python API Script
- Understanding SOC Development and Deployment Models
- Agile Methodology
- DevOps Practices and Principles
- Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
- Essential Windows and Linux CLI for Development and Operations
- Infrastructure as Code
- SOC Platform Development, Engineering, Operation, and Maintenance
- Create Basic Bash Scripts
- Performing Security Analytics and Reports in a SOC
- Security Data and Log Analytic Techniques
- Security Data Management Users
- Security Data with Log Management and Retention
- Security Data and Log Aggregations
- Security Information and Event Management
- Security Data and Log Analytics Automation
- Dashboards and Reports
- Malware Forensics Basics
- Malware Detection Tools
- Static Malware Analysis from Detection Tools
- Dynamic Malware Analysis from Sandbox Logs
- File Fingerprinting for Attribution
- Evading Detection
- File Forensics
- Reverse Engineer Malware
- Threat Hunting Basics
- Proactive Threat Hunting Concepts
- Using MITRE ATTACK® Framework for Threat Hunting
- Using CAPEC to Hunt for Weaknesses in Applications
- Evaluating Security Posture and Gaps in Controls Using MITRE ATTACK®
- Threat Hunting Case Study
- Perform Threat Hunting
- Performing Incident Investigation and Response
- Threat Modeling
- Indicators of Compromise and Indicators of Attack
- Attack Campaigns, Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures
- Sequence of Events During an Attack Based on Analysis of Traffic Patterns
- Steps to Investigate the Common Types of Cases
- IRT Concepts and Actions
- Tool-Based Mitigation and Gaps
- Steps to Investigate Potential Data Loss
- Conduct an Incident Response
- Lessons Learned
Attività Laboratoriali
- Explore Cisco SecureX Orchestration
- Explore Splunk Phantom Playbooks
- Examine Cisco Firepower Packet Captures and PCAP Analysis
- Validate an Attack and Determine the Incident Response
- Submit a Malicious File to Cisco Threat Grid for Analysis
- Endpoint-Based Attack Scenario Referencing MITRE ATTACK®
- Evaluate Assets in a Typical Enterprise Environment
- Explore Cisco Firepower NGFW Access Control Policy and Snort Rules
- Investigate IOCs from Cisco Talos Blog Using Cisco SecureX
- Explore the ThreatConnect Threat Intelligence Platform
- Track the TTPs of a Successful Attack Using a TIP
- Query Cisco Umbrella Using Postman API Client
- Fix a Python API Script
- Create Basic Bash Scripts
- Reverse Engineer Malware
- Perform Threat Hunting
Tipologia
Corso di Formazione con Docente
Docenti
I docenti sono Istruttori accreditati CISCO e certificati in altre tecnologie IT, con anni di esperienza pratica nel settore e nella Formazione.
Infrastruttura laboratoriale
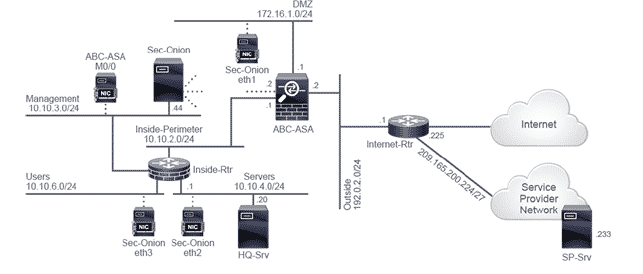
Per tutte le tipologie di erogazione, il Corsista può accedere alle attrezzature e ai sistemi reali Cisco presenti nei Nostri laboratori o direttamente presso i data center Cisco in modalità remota h24. Ogni partecipante dispone di un accesso per implementare le varie configurazioni avendo così un riscontro pratico e immediato della teoria affrontata. Ecco di seguito alcune topologie di rete dei Laboratori Cisco Disponibili:
Dettagli del corso
Prerequisiti
Si consiglia la partecipazione al Corso Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Associate.
Durata del corso
- Durata Intensiva 5gg;
Frequenza
Varie tipologie di Frequenza Estensiva ed Intensiva.
Date del corso
- Corso Cisco CBRCOR (Formula Intensiva) – Su Richiesta – 9:00 – 17:00
Modalità di iscrizione
Le iscrizioni sono a numero chiuso per garantire ai tutti i partecipanti un servizio eccellente.
L’iscrizione avviene richiedendo di essere contattati dal seguente Link, o contattando la sede al numero verde 800-177596 o inviando una richiesta all’email [email protected].


